By Hon. Prof. Kariuki Muigua, OGW, PhD, C.Arb, FCIArb is a Professor of Environmental Law and Dispute Resolution at the University of Nairobi, Member of Permanent Court of Arbitration, Leading Environmental Law Scholar, Respected Sustainable Development Policy Advisor, Top Natural Resources Lawyer, Highly-Regarded Dispute Resolution Expert and Awardee of the Order of Grand Warrior (OGW) of Kenya by H.E. the President of Republic of Kenya. He is the Academic Champion of ADR 2024, the African ADR Practitioner of the Year 2022, the African Arbitrator of the Year 2022, ADR Practitioner of the Year in Kenya 2021, CIArb (Kenya) Lifetime Achievement Award 2021 and ADR Publisher of the Year 2021 and Author of the Kenya’s First ESG Book: Embracing Environmental Social and Governance (ESG) tenets for Sustainable Development” (Glenwood, Nairobi, July 2023) and Kenya’s First Two Climate Change Law Book: Combating Climate Change for Sustainability (Glenwood, Nairobi, October 2023), Achieving Climate Justice for Development (Glenwood, Nairobi, October 2023), Promoting Rule of Law for Sustainable Development (Glenwood, Nairobi, January 2024) and Actualizing the Right to a Clean and Healthy Environment (Glenwood, Nairobi, March 2024)*
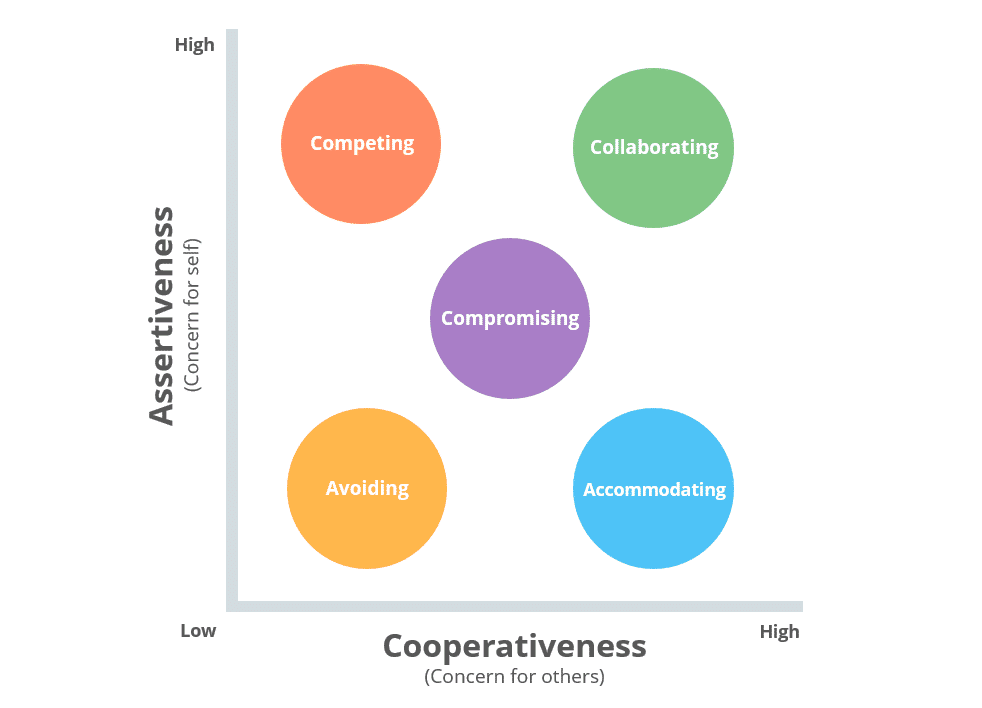
Conflict management can involve different approaches. These techniques include collaborating, competing, avoiding, accommodating, and compromising. Collaborative approaches towards conflict management have been hailed as the most ideal due to their potential to produce satisfactory and long-term results. Collaborative approaches have been hailed as ensuring efficient and effective management of conflicts towards peace and sustainability.
Collaborative conflict management refers to the use of a wide range of informal approaches where competing or opposing stakeholder groups work together to reach an agreement on a controversial issue. In addition, it has been pointed out that collaborative conflict resolution encourages teams to work through disagreements through empathy, listening, and mutually beneficial solutions. Collaboration, unlike compromise, does not focus on both sides making sacrifices. Instead, in collaborative approaches, both parties come up with mutually beneficial solutions. Collaborating has been identified as a powerful approach to conflict resolution built on cooperation, open communication, and finding win-win outcomes.
It has been argued that among all conflict management techniques, collaborative approaches are the most likely to identify the root cause of a conflict, pinpoint the underlying needs of the parties involved, and come to a win-win outcome for everyone. Through collaboration, all parties to a conflict come together to openly discuss the issue causing tension, actively listen to each other, and work towards a solution that is mutually satisfactory and acceptable to everyone.
It has been pointed out that collaborative conflict management aims to achieve several objectives which include: promoting the participation of diverse or competing stakeholder groups in order to reach agreement on a controversial issue; assisting stakeholders in adopting an attitude that is oriented towards cooperation rather than pursuit of individual interests; establishing new forms of communication and decision making on important issues, and raising awareness of the importance of equity and accountability in stakeholder communication; developing partnerships and strengthening stakeholder networks; creating space for stakeholders to communicate in order to bring about future agreements so that concrete action can be taken; and producing decisions that have a strong base of support.
In addition, it has been observed that collaborative approaches towards conflict management aim to preserve relationships, build trust, and promote long term positive change. Collaborative conflict management is based on certain principles key among them being ensuring open communication, finding common ground, and creating a culture of trust. Collaborative approaches towards conflict management has been hailed as the “win-win” strategy to conflict management. It is an effective means of restoring peace.
Further, it has been argued that collaborative approaches are a better way to conflict management since they encourage freedom of expression, where the conflicting parties express their thoughts and concerns verbally, which makes all parties involved in the dispute feel valued and be aware of each other’s concern. In addition, it has been argued that collaborating sets the tone for future conflict resolution and gives those involved the shared responsibility to manage conflicts prior to escalation.
Managing conflicts in a collaborative way helps to develop trust and strengthen communication channels between the various parties. For example, it has been pointed out that in conflicts related to natural resources, collaborative approaches help in generating inclusive solutions that arise from wider stakeholders’ views, and therefore helps clarify policies, institutions and processes that regulate access to – or control over – natural resources. It has been observed that collaborating entails all parties to a conflict sitting down together, discussing the conflict, and working towards a solution together.
Collaborative approaches towards conflict management have been identified as vital when it is necessary to maintain all parties’ relationships or when the solution itself will have a significant impact on large group of people. In such situations, collaborating ensures a win-win solution is found so that everyone is satisfied which creates the condition for peace and sustainability.
It has been pointed out that for collaborative approaches to be effective, it is necessary for all parties to have collaborating skills such as the ability to use active or effective listening, confront situations in a nonthreatening way, analyze input, and identify underlying concerns. Collaborative approaches towards conflict management are important in fostering effective and long-lasting outcomes. It is therefore necessary to apply collaborative approaches in order to ensure effective and efficient management of conflicts.
*This is an extract from Kenya’s First Clean and Healthy Environment Book: Actualizing the Right to a Clean and Healthy Environment (Glenwood, Nairobi, January 2024) by Hon. Prof. Kariuki Muigua, OGW, PhD, Professor of Environmental Law and Dispute Resolution, Senior Advocate of Kenya, Chartered Arbitrator, Kenya’s ADR Practitioner of the Year 2021 (Nairobi Legal Awards), ADR Lifetime Achievement Award 2021 (CIArb Kenya), African Arbitrator of the Year 2022, Africa ADR Practitioner of the Year 2022, Member of National Environment Tribunal (NET) Emeritus (2017 to 2023) and Member of Permanent Court of Arbitration nominated by Republic of Kenya and Academic Champion of ADR 2024. Prof. Kariuki Muigua is a foremost Environmental Law and Natural Resources Lawyer and Scholar, Sustainable Development Advocate and Conflict Management Expert in Kenya. Prof. Kariuki Muigua teaches Environmental Law and Dispute resolution at the University of Nairobi School of Law, The Center for Advanced Studies in Environmental Law and Policy (CASELAP) and Wangari Maathai Institute for Peace and Environmental Studies. He has published numerous books and articles on Environmental Law, Environmental Justice Conflict Management, Alternative Dispute Resolution and Sustainable Development. Prof. Muigua is also a Chartered Arbitrator, an Accredited Mediator, the Managing Partner of Kariuki Muigua & Co. Advocates and Africa Trustee Emeritus of the Chartered Institute of Arbitrators 2019-2022. Prof. Muigua is a 2023 recipient of President of the Republic of Kenya Order of Grand Warrior (OGW) Award for his service to the Nation as a Distinguished Expert, Academic and Scholar in Dispute Resolution and recognized among the top 5 leading lawyers and dispute resolution experts in Band 1 in Kenya by the Chambers Global Guide 2024 and was listed in the Inaugural THE LAWYER AFRICA Litigation Hall of Fame 2023 as one of the Top 50 Most Distinguished Litigation Lawyers in Kenya and the Top Arbitrator in Kenya in 2023.
References
Bercovitch. J., ‘Conflict and Conflict Management in Organizations: A Framework for Analysis.’ Available at https://ocd.lcwu.edu.pk/cfiles/International%20Relations/EC/IR403/Conflict.ConflictManagementinOrga nizations.pdf (Accessed on 01/03/2024).
Bercovitch. J., ‘Mediation Success or Failure: A Search for the Elusive Criteria.’ Cardozo Journal of Conflict Resolution, Vol. 7, p 289.
Bloomfield. D., ‘Towards Complementarity in Conflict Management: Resolution and Settlement in Northern Ireland,’ Journal of Peace Research., Volume 32, Issue 2.
Burrell. B., ‘The Five Conflict Styles’ Available at https://web.mit.edu/collaboration/mainsite/ modules/module1/1.11.5.html (Accessed on 01/03/2024).
Demmers. J., ‘Theories of Violent Conflict: An Introduction’ (Routledge, New York, 2012).
Diana. M., ‘From Conflict to Collaboration’ Available at https://www.pmi.org/learning/library/conflict-collaboration-beyond-projectsuccess-1899 (Accessed on 01/03/2024).
Food and Agriculture Organization., ‘Collaborative Conflict Management for Enhanced National Forest Programmes (NFPs)’ Available at https://www.fao.org/3/i2604e/i2604e00.pdf (Accessed on 01/03/2024).
International Organization for Peace Building., ‘Natural Resources and Conflict: A Path to Mediation.’ Available at https://www.interpeace.org/2015/11/naturalresources-and-conflict-a-path-to-mediation/ (Accessed on 01/03/2024).
Isenhart. M.W., & Spangle. M., ‘Summary of “Collaborative Approaches to Resolving Conflict” ‘ Available at https://www.beyondintractability.org/bksum/isenhart-collaborative (Accessed on 01/03/2024).
Kaushal. R., & Kwantes. C., ‘The Role of Culture and Personality in Choice of Conflict Management Strategy.’ International Journal of Intercultural Relations 30 (2006) 579– 603.
Leeds. C.A., ‘Managing Conflicts across Cultures: Challenges to Practitioners.’ International Journal of Peace Studies, Volume 2, No. 2, 1997.
May. E., ‘Collaborating Conflict Style Explained In 4 Minutes’ Available at https://www.niagara institute.com/blog/collaborating-conflict-style/ (Accessed on 01/03/2024).
Miroslavov. M., ‘Mastering the Collaborating Conflict Style In 2024’ Available at https://www.officernd.com/blog/collaborating-conflictstyle/#:~:text=It’s%20one%20of%20the%20strat egies,their%20underlying%20needs %20and%20interests. (Accessed on 01/03/2024).
Muigua. K & Kariuki. F., ‘ADR, Access to Justice and Development in Kenya.’ Available at http://kmco.co.ke/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/ADR-access-tojustice-and-development-inKenyaRevised-version-of-20.10.14.pdf (Accessed on 01/03/2024).
Muigua. K., ‘Alternative Dispute Resolution and Access to Justice in Kenya.’ Glenwood Publishers Limited, 2015.
Muigua. K., ‘Reframing Conflict Management in the East African Community: Moving from Alternative to ‘Appropriate’ Dispute Resolution.’ Available at https://kmco.co.ke/wpcontent/uploads/2023/06/ Reframing-ConflictManagement-in-the-East-African-CommunityMoving-from-Alternative-toAppropriate-Dispute-Resolution (Accessed on 01/03/2024).
Muigua. K., ‘Resolving Conflicts through Mediation in Kenya.’ Glenwood Publishers Limited, 2nd Edition., 2017.
Quain. S., ‘The Advantages & Disadvantages of Collaborating Conflict Management’ Available at https://smallbusiness.chron.com/advantagesdisadvantages-collaborating-conflict-management-36052.html (Accessed on 01/03/2024).
Samuel. A., ‘Is the Collaborative Style of Conflict Management the Best Approach?’ Available at https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/collaborative-style-conflictmanagement-best-approach-samuel-ansah (Accessed on 01/03/2024).
United Nations., ‘Land and Conflict’ Available at https://www.un.org/en/landnatural-resources-conflict/pdfs/GN_ExeS_Land%20and%20Conflict.pdf (Accessed on 01/03/2024).
Weiss. J., & Hughes. J., ‘Want Collaboration?: Accept—and Actively Manage— Conflict’ Available at https://hbr.org/2005/03/want-collaboration-accept-andactively-manage-conflict (Accessed on 01/03/2024).




 Lawyers1 year ago
Lawyers1 year ago
 News & Analysis3 years ago
News & Analysis3 years ago
 News & Analysis3 years ago
News & Analysis3 years ago
 Lawyers1 year ago
Lawyers1 year ago
 News & Analysis2 years ago
News & Analysis2 years ago
 News & Analysis1 year ago
News & Analysis1 year ago
 News & Analysis3 years ago
News & Analysis3 years ago
 News & Analysis1 year ago
News & Analysis1 year ago